Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are a population of cells with a single nucleus in peripheral blood, mainly composed of lymphocytes (including T cells, B cells and NK cells) in different proportions, monocytes and a small amount of other types of cells. As a key component of the innate and adaptive immune systems, PBMCs can protect the body from infection by viruses, bacteria and parasites and invasion of foreign bodies, and have the ability to eliminate tumor cells. Therefore, PBMCs are widely used in immunology, infectious diseases, oncology, vaccine development, transplantation therapy, personalized medicine and toxicology, and are important biomaterials in basic experimental research.

Till now, the main methods for isolating PBMCs include Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient centrifugation and Percoll method. This article will focus on the experimental principle and operation steps of the Ficoll method.
Density gradient centrifugation achieves separation through the density difference between different substances. PBMCs differ from other blood cells in volume, morphology, density and other characteristics. When density gradient centrifugation is performed using a layering fluid with a density of 1.075 g/mL to 1.092 g/mL and close to isotonicity, various types of cells will be distributed in the gradient according to their own density, thereby achieving the separation of blood cells.
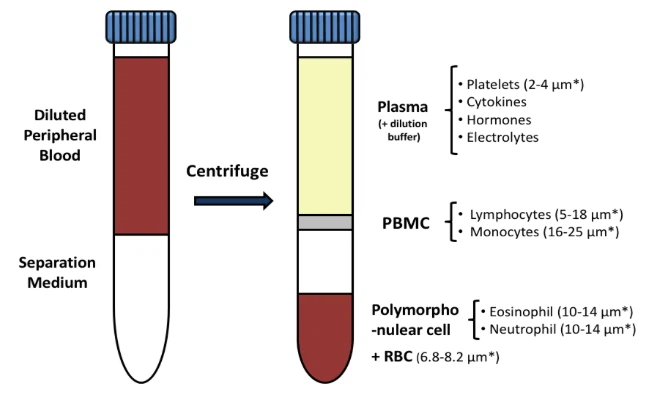
The commonly used layering liquid polysucrose-diatrizoate is a synthetic sucrose polymer called Ficoll, with a molecular weight of 40kD, and has the characteristics of high density, low osmotic pressure and non-toxicity. High-concentration Ficoll solution has high viscosity and is prone to cell aggregation, so a low-concentration solution of 60g/L (density of 1.020) is usually used, and urografin with a specific gravity of 1.200 is added to increase the density. A suitable layering liquid can be prepared by adding an appropriate amount of 340g/L urografin.
When used to separate human peripheral lymphocytes, the optimal density of the layering fluid is 1.077±0.001, because the density of human red blood cells is about 1.093, granulocytes is 1.092, mononuclear cells are between 1.076 and 1.090, and the density of platelets is 1.030g/mL~1.035g/mL. During the separation process, the layering fluid is placed at the bottom of the test tube, and then the heparinized whole blood appropriately diluted with Hanks solution or PBS solution is gently superimposed on the layering fluid to form a clear interface. After horizontal centrifugation, different layers of liquid and cell bands will appear in the centrifuge tube. Because the density of red blood cells and granulocytes is greater than that of the layering fluid, and red blood cells are easily aggregated into strings under the action of Ficoll and deposited at the bottom of the tube. Platelets are suspended in plasma due to their low density, while mononuclear cells form a white film at the interface between the plasma layer and the layering fluid. After absorbing this layer of cells, washing and resuspending, mononuclear cells can be obtained.
The purity of mononuclear cells separated by this method can reach 95%, of which lymphocytes account for about 90% to 95%. The cell recovery rate exceeds 80% and is closely related to room temperature. When the temperature exceeds 25°C, the cell recovery rate will be reduced.

A low-speed refrigerated centrifuge is usually required for PBMC separation experiments. The following are the specific requirements for the centrifuge:
Low-speed freezing function: PBMC separation requires a lower centrifugal speed, usually between 400-1000g, and the temperature is kept at around 4°C to avoid heat damage to the cells.
Horizontal rotor: When using a horizontal rotor, the cell stratification is clearer, and the specific choice can be based on the experimental needs.
The choice of centrifuge is crucial to effectively protect the integrity of PBMC cells and ensure high-purity separation results.
Equipment, consumables and reagents required for PBMC isolation experiment
Equipment
●Biological safety cabinet
●Low-speed refrigerated centrifuge
●Hemocytometer
●Microscope
Consumables
●Vacuum blood collection tube (ACD/EDTA/heparin anticoagulation)
●Centrifuge tube
●Pipette
●Sterile pipette tip
●Cryotube
●Pipette
Reagents
●PBS buffer
●RPMI-1640 culture medium
●Fetal bovine serum
●DMSO (for cell preservation)
●Lymphocyte separation solution (density 1.077±0.001g/mL at 20°C)
●Trypan blue staining solution
Specific steps:
●Collect peripheral blood
I. Aseptically collect fresh peripheral blood into a vacuum blood collection tube containing ACD, EDTA or heparin anticoagulant.
II. After the blood is collected, PBMC separation should be performed as soon as possible to ensure cell activity and separation effect.
●Isolate PBMC
Select an appropriate centrifuge tube according to the amount of blood sample to ensure that the separation system is appropriate. You can refer to the following experimental system:
Whole blood volume < 3 mL, use 15 mL centrifuge tube
6 mL < whole blood volume < 10 mL, use 50 mL centrifuge tube
Other volumes can be adjusted to the appropriate tube diameter according to needs

Separation steps:
I. Add an equal volume of PBS to dilute the blood in the anticoagulation tube containing whole blood (0.1% PBSA or saline can be used as an alternative diluent).
II. Take a new 15 mL centrifuge tube and add lympholyte H lymphocyte separation solution (generally, the volume ratio of diluted blood to layering solution is 2:1 to 3:1). Slowly superimpose the diluted peripheral blood on the lymphocyte separation solution along the inclined tube wall to ensure that a clear layer is formed (the upper layer is the blood diluent and the lower layer is the lymphocyte separation solution).
III. Centrifuge (800g, 20 minutes, room temperature), try to set the acceleration and deceleration of the centrifuge to low speed (1 for acceleration, 0 for deceleration) to prevent the vibration at the end of centrifugation from disturbing the stratification. After centrifugation, the centrifuge tube is divided into four layers (from top to bottom):
Plasma layer: contains platelets and broken cells.
Mononuclear cell buffy coat layer: mainly PBMC (mononuclear cells), a narrow white cloudy band.
Separation fluid layer
Red blood cell and granulocyte layer
IV. Aspirate the top layer of plasma, transfer the buffy coat layer (PBMC layer) to a new centrifuge tube, add an appropriate amount of PBS, and use a pipette to blow evenly to fully wash the cell pellet. Centrifuge (800g, 10 minutes, room temperature), and discard the supernatant. Wash twice in total.
V. After washing, wash again with PBS, centrifuge (200g, 7 minutes, room temperature), and discard the supernatant to remove platelets.
VI. If mixed with red blood cells, add red blood cell lysis buffer, incubate at 37°C for 5 minutes, wash again with PBS and centrifuge (200g, 7 minutes, room temperature).
VII. Resuspend the cell pellet in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% inactivated calf serum and count the cells.
●PBMC processing
PBMCs are seeded into culture plates or culture bottles at a certain density, or frozen for future use according to experimental requirements.

Practical tips: Precautions in PBMC separation experiments
Sample collection
Peripheral blood is collected using sterile anticoagulant tubes to ensure that the blood does not coagulate and affect the separation effect.
The freshness of the blood is extremely important. It is recommended to perform PBMC separation within 24 hours after collection to maintain cell viability and separation effect.
Hemodilution
Dilution of blood can reduce viscosity and red blood cell aggregation, thereby increasing the yield of mononuclear cells. PBS, 0.1% PBSA or saline can be used as diluents.
Experimental temperature
Room temperature (18-25°C) is the ideal operating temperature, because temperature changes can affect the density of the layering fluid, which in turn affects the separation efficiency.
The layering fluid should be preheated to room temperature before use to avoid excessive loss of lymphocytes due to low temperature or excessive loss of cell activity due to high temperature.
Adjustment of centrifugation parameters
The centrifugation speed and time should be adjusted according to the sample situation. If red blood cells are mixed in the buffy coat, the speed can be appropriately increased or the centrifugation time can be extended; if more lymphocytes are lost, the speed can be reduced or the centrifugation time can be shortened.
How to add the layering solution
The layering solution should be added slowly to the bottom of the centrifuge tube to prevent infiltration around it. When superimposing the blood suspension, gentle operation is required to form a clear interface to avoid disturbing the layering and affecting the separation effect.
Gentle operation
The operation process should be as gentle as possible to avoid mechanical damage to the cells. At the same time, the total duration of the experiment should be shortened to maintain cell viability.
Estimation of the number of PBMCs
Usually, 1 mL of peripheral blood contains about 1-2 x 10⁶ PBMCs, but there are differences between different individuals.
Cell composition and purity
Although this method can recover PBMCs with higher purity and viability, a small amount of other cell components will still be mixed. Most of the PBMCs are lymphocytes, including B cells and T cells, of which T cells (CD3⁺) account for 45-70% of lymphocytes, most of which are in the initial (naive) state and are not activated by antigens.
The proportion of monocytes is 10-30%, which will differentiate into dendritic cells (DC) or macrophages under appropriate stimulation.
The proportion of stem cells is extremely low, only 0.1-0.2%, so it is difficult to separate them from whole blood by this method.
These details will help optimize the PBMC separation experiment, improve the recovery rate and purity of cells, and provide high-quality cell samples for subsequent experiments.
In the PBMC separation experiment, the low-speed refrigerated centrifuge plays a vital role. It can provide stable low-speed centrifugation conditions and effectively avoid cell loss caused by excessive centrifugation speed or temperature fluctuations. The precise control ability of the low-speed refrigerated centrifuge ensures the accuracy and purity of cell separation, especially in the PBMC separation process, it can ensure the integrity of the cell layer, thereby achieving efficient and repeatable experimental results. Therefore, choosing a low-speed refrigerated centrifuge with stable performance and precise temperature control is a key equipment to ensure the smooth progress of PBMC separation experiments and obtain high-quality cell samples.

+86 21 51096910

sales@welsobio.com
marketing@welsobio.com
1-1009, National Industrial Design Park, No. 599 Jianzhu Road, Binhu, Wuxi , Jiangsu, China, 214062
Head Office: No. 439 Jinglian Road, Minhang District, Shanghai,China, 201108